A Vertical Form Fill Seal machine (VFFS) is an automated packaging system that forms bags from a continuous roll of film, fills them with product, and seals them shut. In a VFFS machine, flat packaging film (often plastic or laminated) is fed into the machine, wrapped around a vertical forming tube, and sealed along its edges to create a continuous bag tube. Product (such as powders, granules, snacks, or liquids) is then dispensed into the open bag. The top of the bag is then heat-sealed to complete the package.
This form-fill-seal process is extremely versatile. VFFS machines can handle both solid and liquid products reliably – industry sources note that “both solids and liquids can be bagged” on VFFS equipment. The VFFS concept dates back to a 1936 patent by Walter Zwoyer, and today these machines are used worldwide for high-speed packing of foods, pet products, chemicals, and more. Packaging specialists note that VFFS systems offer “durable, versatile packaging automation” for both food and non-food applications.
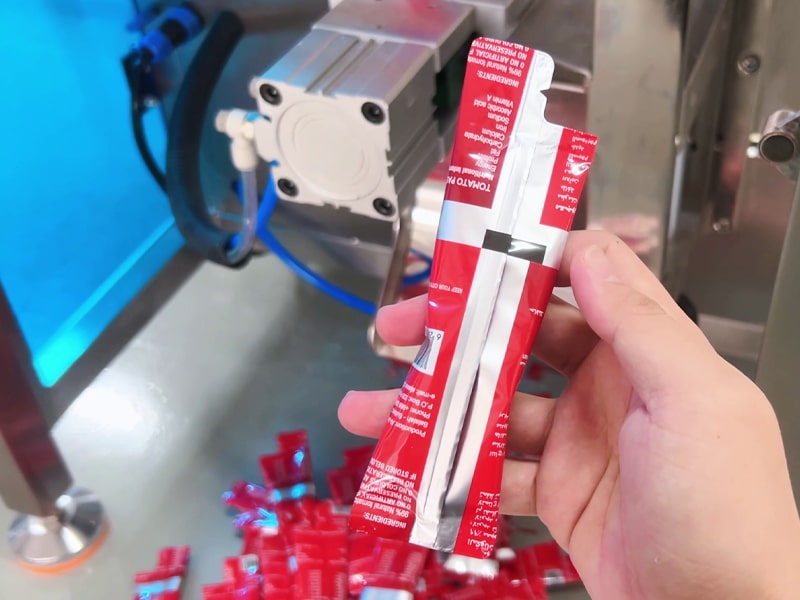
Terminology: In industry, a VFFS machine may also be called a vertical bagger or simply a form-fill-seal machine (when referring to the vertical style). Any machine that “forms, fills, and seals” packages is a form-fill-seal system, and VFFS indicates the vertical orientation. Other names include vertical form-fill-and-seal machine, vertical form filling machine, or vertical form seal machine. In all cases, the emphasis is on an integrated assembly-line process that forms the bag from film, fills it with product, and seals it in one continuous cycle.
How VFFS Machines Work
A VFFS machine automates the packaging process in a compact, vertical layout. The basic operating steps are:
- Film Unwinding and Guiding: A large roll of packaging film is mounted on the machine. Rollers and tensioners feed the film into the machine while keeping it smooth and aligned.
- Forming the Bag: The flat film passes over a shaping device (forming tube). The film is wrapped into a vertical tube. A long vertical sealing jaw presses and heats the film edges, sealing them into a fin seal and thus forming a continuous vertical tube.
- Bottom Sealing: Before filling, the bottom of the film tube is closed off. A horizontal sealing bar applies heat and pressure to create the bottom seal of the bag. This may occur intermittently (stopping the film to seal) or continuously as the film moves, depending on machine design.
- Product Filling: With the bag opened at the top, the machine dispenses product into it. The filling method varies by product: small solids or snacks may be weighed and dropped by a scale feeder, powders by auger fillers, and liquids by pump or volumetric fillers. Fill sensors ensure each bag receives the correct weight or volume.
- Top Sealing and Cutting: After filling, a horizontal sealing jaw closes to form the top seal of the bag and the bottom of the next bag. The same jaw usually includes a cutter that cuts the filled bag free from the tube. Thus the bag is sealed and separated in one action.
- Bag Discharge: The finished pouch is discharged onto an exit conveyor. The cycle immediately repeats with the forming of a new bag below.
This continuous cycle can produce hundreds of bags per minute, depending on the bag size and product flow. Precise electronic controls synchronize the film feed, sealing times, and fill quantities. For example, sensors track film position for accurate cutting, and dosing systems ensure consistent fill weights.
Optional Features: Many VFFS lines include extras to enhance packaging. Integrated printers can stamp dates or batch codes on the film, and gas-flushing units can inject inert gas (e.g. nitrogen) into the pouch before sealing to extend shelf life. Machines can also be fitted with tear notches, zippers, or handles. All these functions occur inline as part of the continuous form-fill-seal cycle.
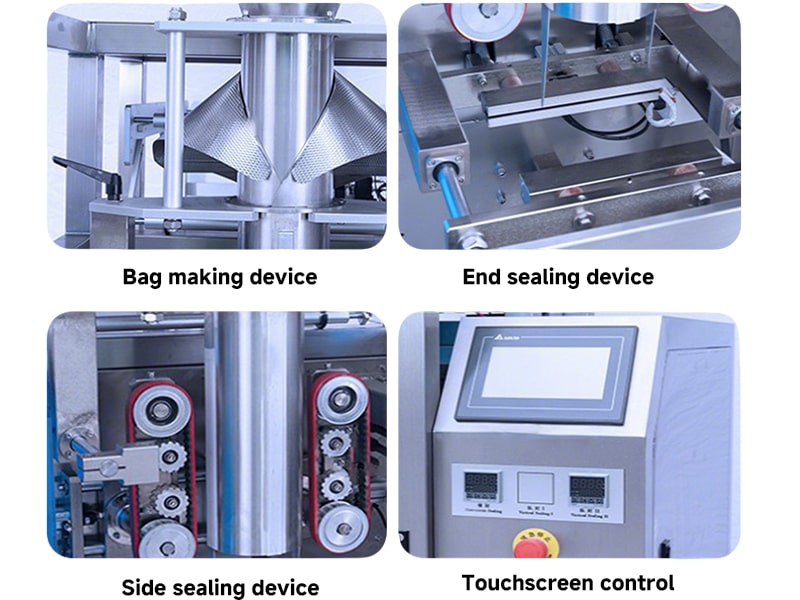
Key Components of a VFFS Machine
A VFFS machine consists of several interlinked subsystems:
- Film Unwind and Tension Control: Holds the film roll and feeds film into the machine. Rollers and sensors maintain proper tension and alignment.
- Forming Tube and Collar: A hollow metal tube (often with an adjustable collar) that shapes the film into a tubular form. The diameter of this tube sets the bag width.
- Vertical Sealing Bars: Long heated jaws that run alongside the forming tube. They clamp the film edges and apply heat/pressure to create a continuous vertical seal.
- Horizontal Sealing and Cutting Jaws: A pair of jaws that seal across the film to form bag tops and bottoms. A built-in knife or hot wire then separates the finished bag from the film.
- Filling System: Equipment that dispenses product into each bag. Common devices include multi-head weighers for bulk solids, auger or piston fillers for powders, and pump fillers for liquids.
- Control System: The programmable logic controller (PLC) or computer that controls machine functions. Operators input parameters (bag length, fill weight, speed) via a touchscreen interface.
- Auxiliary Attachments: Conveyors (infeed for product, discharge for bags), printers/coders, gas flush systems, and safety guards.
Each component must work in concert to ensure smooth operation. For example, proper tension control prevents film wrinkles, and precise sealing pressure ensures consistent, leakproof seals.
Types of VFFS Machines
VFFS machines are available in different configurations:
- Motion Type: Intermittent (stop-start) vs. Continuous. Intermittent machines feed and then pause film for sealing; continuous machines keep the film moving while a moving seal bar closes the bag. Continuous-motion VFFS machines achieve higher speeds (often hundreds of bags per minute), while intermittent machines are simpler and can handle heavier film or product loads.
- Drive System: Pneumatic vs. Servo. Pneumatic VFFS machines use air cylinders to power seals and cutters, offering simplicity and reliability. Servo-driven machines use electric servo motors, providing precise, high-speed motion for the sealing and cutting stages. Servos also allow easier integration with digital controls and robotics.
- Single-Web vs. Dual-Web: Most VFFS machines form bags from a single film web (creating 3-sided or pillow pouches). Dual-web (four-side seal) VFFS machines use two films (one for each bag face), useful for medical or specialty pouches requiring multi-material structures.
- Bag Format: A given VFFS line can often be reconfigured for different bag styles by swapping forming tubes and jaws. Common formats include pillow bags, gusseted (stand-up) bags, quad-seal or flat-bottom bags. Some machines are dedicated to one style, while others allow quick changeovers between formats.
The choice depends on production needs. For example, a small-scale producer might choose an intermittent pneumatic VFFS for cost savings, while a large manufacturer might use a continuous servo-driven VFFS for maximum throughput.
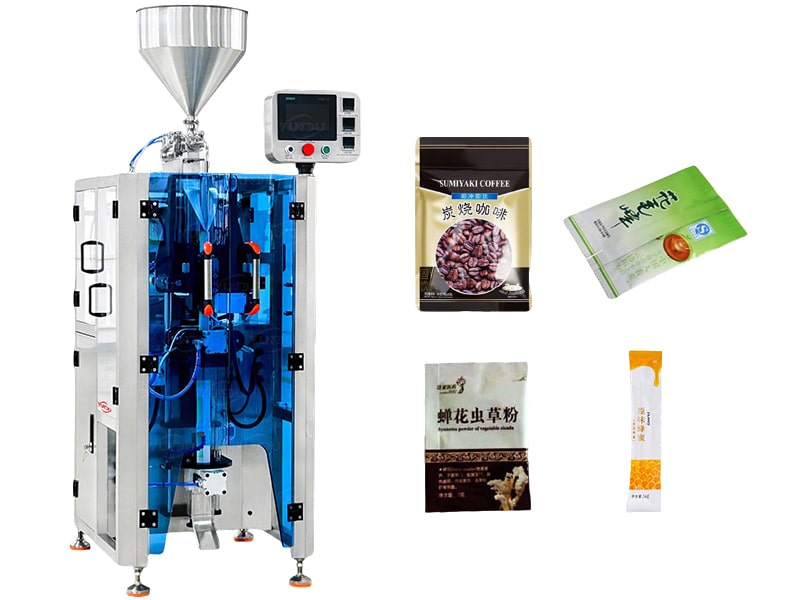 |
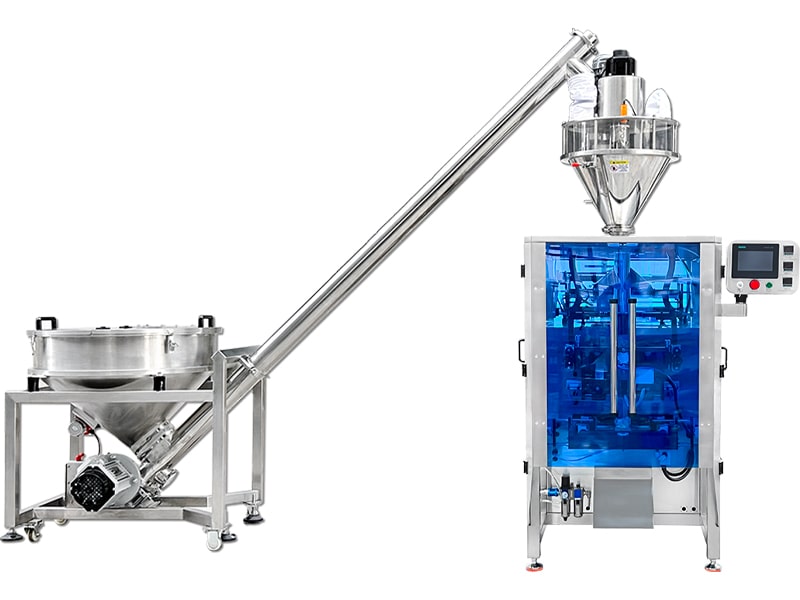 |
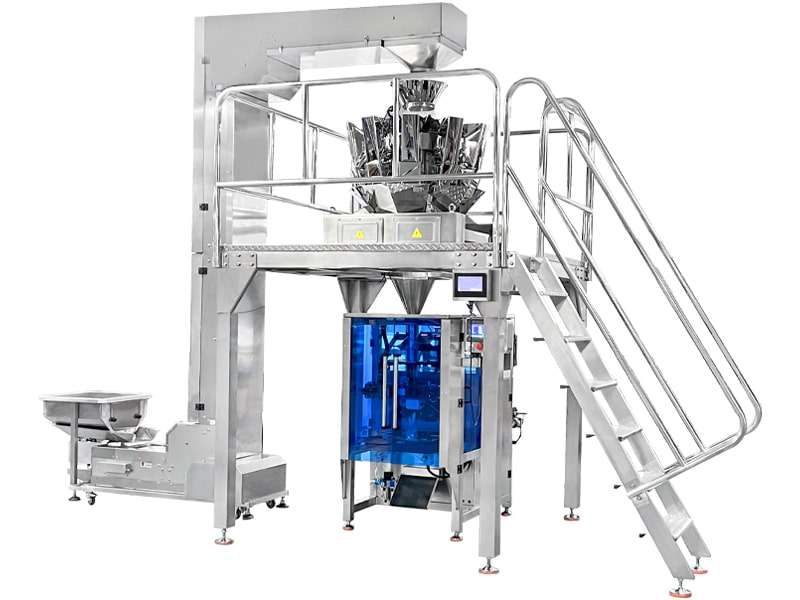 |
| VFFS machine-Small vertical clamp and pull packaging machine | VFFS machine for powder packaging | VFFS machine with electronic scale |
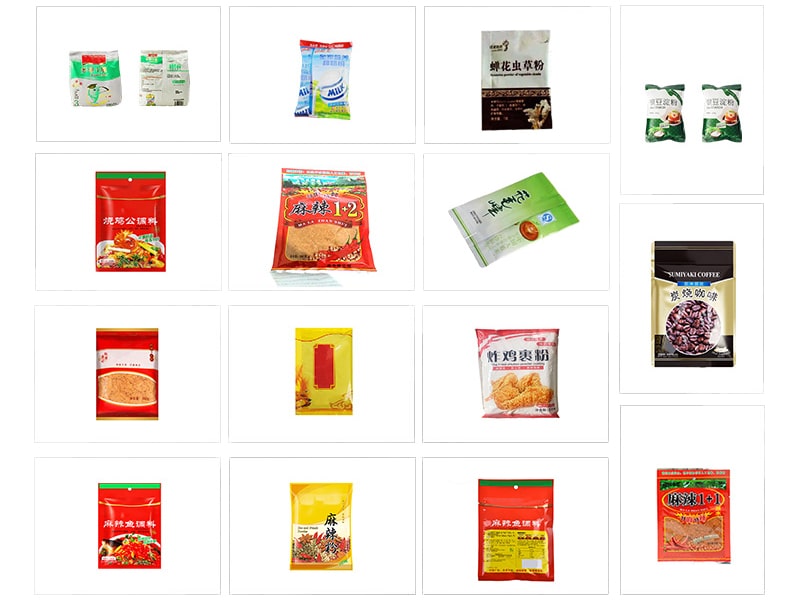
Applications of VFFS Machines
VFFS machines serve a wide range of markets:
- Food Products: Snack foods (chips, popcorn, nuts), candies, dried fruits, cereals, and bakery goods are commonly bagged on VFFS machines. Staples like sugar, salt, spices, rice, and flour are often weighed and packed in pouches. Many frozen foods (e.g. vegetables, pizzas) use VFFS packaging as well.
- Liquids and Sauces: Liquid products such as soups, sauces, juices, and condiments are frequently packaged in pouches by vertical baggers. The vertical orientation simplifies filling of pourable products. Carepac notes that VFFS machines are ideal for liquids that require stable, leak-proof packaging.
- Coffee and Tea: Roasters and tea blenders use VFFS machines for ground coffee, whole beans, and tea leaves. These lines often include gas-flushing to preserve aroma. Even single-serve coffee pods and tea sachets are created by variations of vertical form-fill lines.
- Pet Food: Dry pet foods, treats, and supplements are packaged using VFFS systems. These machines can fill large heavy bags (e.g. dog food) or smaller treat bags, often with integrated resealable zippers or handles.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical: VFFS machines built to sanitary standards can package powders, tablets, and sterile medical supplies in foil or laminated pouches.
- Industrial & Consumer Goods: Products like detergents (powder/liquid), chemicals, hardware (nuts, bolts), and seeds are also bagged on VFFS lines.
- Cosmetics & Specialty: Spa salts, cosmetic powders, herbal mixes, and other specialty items are often packed by VFFS systems.
Because of their versatility, VFFS machines are used for both food and non-food applications.
Advantages of VFFS Packaging
Vertical form-fill-seal systems offer many benefits:
- High Throughput: Automated operation allows very fast production speeds, far beyond manual methods. VFFS lines can produce hundreds of pouches per minute.
- Consistency and Quality: Automation ensures uniform fills and seals. This precision reduces waste and guarantees that every package meets specifications. The result is consistently high-quality packaging.
- Flexibility: A VFFS machine can switch between bag sizes, styles, and materials with quick changeovers. Manufacturers often use tool-less adjustments to minimize downtime when shifting SKUs.
- Compact Footprint: Vertical machines occupy less floor space than many horizontal packers. This compact design is advantageous in facilities with limited space.
- Lower Packaging Costs: Forming bags from rollstock eliminates the need to purchase premade bags. Film rolls are generally cheaper, and less inventory of packaging materials is needed.
- Enhanced Protection: Tightly sealed pouches shield products from moisture and contaminants. Optional features like gas flushing can further preserve freshness, making VFFS ideal for perishable items.
- Material Versatility: VFFS machines accept a wide range of films (polyethylene, laminated foil, biodegradable, etc.). They handle everything from thin snack films to heavy-duty laminates.
- Easy Integration: VFFS lines integrate seamlessly with upstream weighers or fillers and downstream conveyors or case packers, creating a fully automated packaging cell.
By streamlining operations, VFFS machines often deliver a high return on investment. Many manufacturers upgrade to VFFS to meet demand efficiently and reduce costs.
VFFS vs Other Packaging Methods
VFFS is one form of form-fill-seal packaging. For comparison:
- Horizontal Form-Fill-Seal (HFFS): HFFS machines form and seal bags horizontally along a conveyor. They can reach very high speeds for flat, rigid products (like baked goods or bars) but tend to use more floor space. They also handle solids better than liquids. In contrast, VFFS machines excel with loose granules and liquids, and they require a smaller footprint.
- Premade Pouch Fillers: These use premade bags (zipper pouches, pre-formed bags) that are then filled and sealed. This method requires ordering and storing custom bags in advance. VFFS machines eliminate this need by forming pouches on demand from film rolls.
- Manual/Semi-Automatic: Hand-filling and sealing bags is slow and inconsistent. Even semi-automatic machines require manual steps. Fully automated VFFS lines vastly increase throughput and consistency.
The best method depends on the product and production volume. In many cases, VFFS provides an ideal balance of speed, automation, and flexibility.
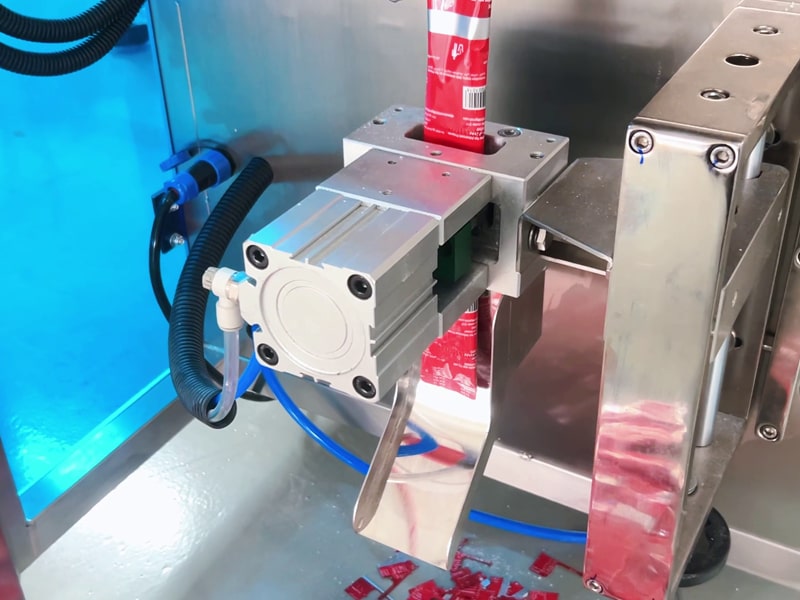
Enhancements and Accessories
Modern VFFS lines often include attachments for added functionality:
- Gas Flushing / MAP: Displacing oxygen with an inert gas (e.g. nitrogen) inside the pouch to extend shelf life.
- Resealable Closures: Built-in slider zippers or tear strips for easy consumer reclosure.
- Tear Notches & Easy-Open: Die-cut notches or perforations for effortless opening.
- Inline Printing: Date/lot coders and label printers integrated into the film path.
- Multi-Head Weighers: Precise filling of multi-ingredient or variable-weight pouches.
- Robotic Integration: Servo-driven VFFS machines can pair with robots for case packing or tray loading.
- Automatic Film Splicing: High-end systems splice a new film roll without stopping the machine.
These features turn a basic VFFS machine into a complete packaging line, outputting finished, labeled pouches ready for packing.
Conclusion
Vertical Form Fill Seal machines have transformed packaging by combining bag forming, filling, and sealing into a single automated process. Industry experts note that VFFS systems deliver unparalleled efficiency and flexibility. They can handle diverse products and formats, and be outfitted with advanced features (like gas flush or zippers) to meet any requirement. In short, VFFS technology remains a cornerstone of high-volume packaging. As manufacturing trends emphasize speed and automation, VFFS systems are likely to remain a workhorse of efficient packaging lines.
FAQ: Vertical Form Fill Seal Machine (VFFS Machine)
1. What is a Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS) Machine?
A VFFS machine is an automated packaging system that forms a bag from flat film, fills it with product, and seals it—vertically. It is widely used in industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals for high-speed packaging.
2. How does a VFFS machine work?
A VFFS machine works by unwinding a film roll, forming it into a vertical bag, sealing the edges, filling the bag with product, then sealing and cutting the top to finish the package—all in one continuous process.
3. What products can be packaged using a VFFS machine?
VFFS machines can package a wide range of products including snacks, coffee, powders, liquids, frozen foods, pet food, detergents, and medical supplies. The machine is highly versatile across both food and non-food industries.
4. What are the key components of a VFFS packaging machine?
Key components include the film unwinder, forming tube, vertical and horizontal sealing jaws, filling system, control system (PLC), and optional features like gas flushing, coders, or resealable zippers.
5. What are the advantages of using a VFFS machine?
VFFS machines offer high-speed operation, consistent packaging quality, flexible bag styles, compact footprint, reduced packaging costs, and easy automation integration. They are ideal for both small and large-scale production.
6. What types of bags can a VFFS machine produce?
Common bag types include pillow pouches, gusseted bags, flat-bottom bags, quad-seal bags, and four-side seal pouches (in dual-web models). Machines can often be adapted to different formats.
7. What is the difference between VFFS and HFFS machines?
VFFS (vertical) machines form and fill bags vertically and are ideal for loose or liquid products. HFFS (horizontal) machines operate horizontally and are better suited for solid items like baked goods or bars.
8. Can VFFS machines handle liquids or powders?
Yes, VFFS machines can be customized with appropriate filling systems—such as auger fillers for powders or pump fillers for liquids—to accurately package different product types.
9. Are VFFS machines suitable for small businesses?
Yes. Entry-level VFFS machines with pneumatic systems are cost-effective and simple to operate, making them suitable for small or medium-sized businesses looking to automate their packaging process.
10. What industries commonly use VFFS packaging?
Industries include food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, pet food, cosmetics, agriculture, and chemicals. The versatility of VFFS machines makes them a popular choice across many sectors.
| References: | |
| 1. | Vertical Form‑Fill‑Seal Machine ——Retrieved from:Wikipedia |
| 2. | Heat‑sealing evaluation and runnability issues of flexible paper materials in a VFFS packaging machine ——Retrieved from:Wiley Online Library |
| 3. | Efficiency Optimization of Continuous Motion VFFS ——Retrieved from:IRJET |
| 4. | Vertical Form-Fill-Seal (VFFS) Machines Market Strategic Growth, Innovation & Investment Trends ——Retrieved from:TowardsPackaging |






Comments