What Is a Semi-Automatic Filling Machine?
A semi-automatic filling machine automates the dosing of products into containers (bottles, jars, tubes, etc.) while still requiring some human involvement. In practice, the operator typically places each empty container under the machine’s nozzle or filling head and initiates the fill cycle, after which the machine dispenses a precise volume and prompts the operator to replace the filled container. These machines are a middle ground between fully manual and fully automatic fillers: they increase speed and accuracy over manual filling, yet are more affordable and flexible than a full automation line. Semi-automatic fillers are especially popular in small-to-medium scale production where moderate throughput and versatile changeovers are needed.
Semi-automatic filling machines are classified by the type of product they handle (liquid, paste, powder) and by their drive mechanism (electric or pneumatic). For example, semi-automatic liquid filling machines can accurately dispense water-like fluids such as water, juices, oils and thin gels, as well as thicker syrups and lotions. Paste filling machines (also semi-automatic) are built for high-viscosity products like honey, sauces, creams, and gels. Powder or auger fillers use a rotating screw or auger to measure powders and granules (flour, sugar, spices) into containers. Many semi-auto fillers come in pneumatic versions that use compressed air to drive pistons or valves; these “air-driven” machines are ideal for flammable or explosion-proof environments, as they have no electrical parts in the filling zone and can achieve very precise, drip-free fills.
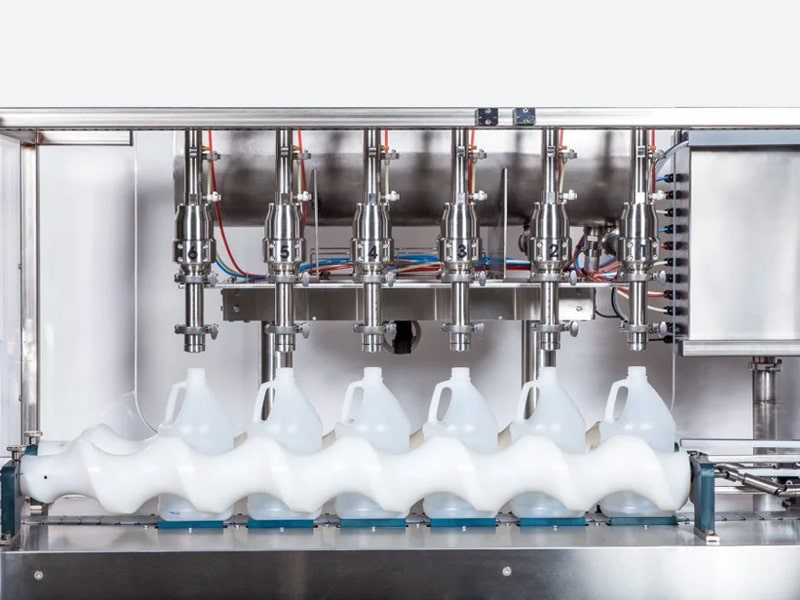
Modern semi-automatic bottle fillers often have multiple heads to speed up production. In this example below, six nozzles dispense liquid into plastic jugs. The operator slides empty jugs into place, starts the fill cycle, and then moves filled jugs out – combining some manual handling with automated dispensing. Semi-automatic bottle filling machines are a common subtype: they are designed to fill bottles (plastic, glass, aluminum, etc.) and can handle a wide range of container shapes and sizes. Despite requiring manual loading and unloading of bottles, these machines use precise pumps or valves so that each bottle gets the correct fill amount without overflowing. This “bench-top” or tabletop format makes them well-suited for businesses that want flexibility and accuracy without the high cost of a full rotary line.

Key Features
Semi-automatic filling machines combine mechanical/electrical automation with operator control. Key advantages and features include:
- Operator control for precision: The operator can start/stop and adjust the filling process, ensuring each container receives the exact target volume. Many machines have digital counters or displays for fine-tuning the fill volume.
- Versatility: They can handle different product types (free-flowing liquids, thick pastes, powders or granules) by swapping pump types or nozzles. For example, piston pumps or peristaltic pumps may be used for fluids, while auger screws meter out powders.
- Cost-effectiveness: Semi-automatic units have a much lower price point and smaller footprint than fully automatic machines. They are ideal for small and medium batches, where the production volume doesn’t justify a fully automated line.
- Ease of use: These machines are relatively simple to set up and operate. They often have user-friendly controls (buttons or foot pedals) and require minimal training.
- Easy maintenance: With fewer complex components (especially pneumatic models), routine cleaning and upkeep can usually be handled by the operator. This reduces downtime and service costs.
How It Works
In a typical semi-automatic filler, the production cycle is shared between the machine and the operator. First, the operator places an empty container (bottle, jar, tube, etc.) on the machine’s platform or slide under the fill nozzle. The operator then activates the machine (e.g. via a foot switch or start button) to begin the cycle. The machine’s pump or valve dispenses a preset volume of product into the container. During dispensing, special nozzles or valves often prevent drips and ensure a clean fill. Once the fill is complete, the operator removes the filled container and loads the next empty one. This cycle is repeated for each container.
The dispensing mechanism varies by product type:
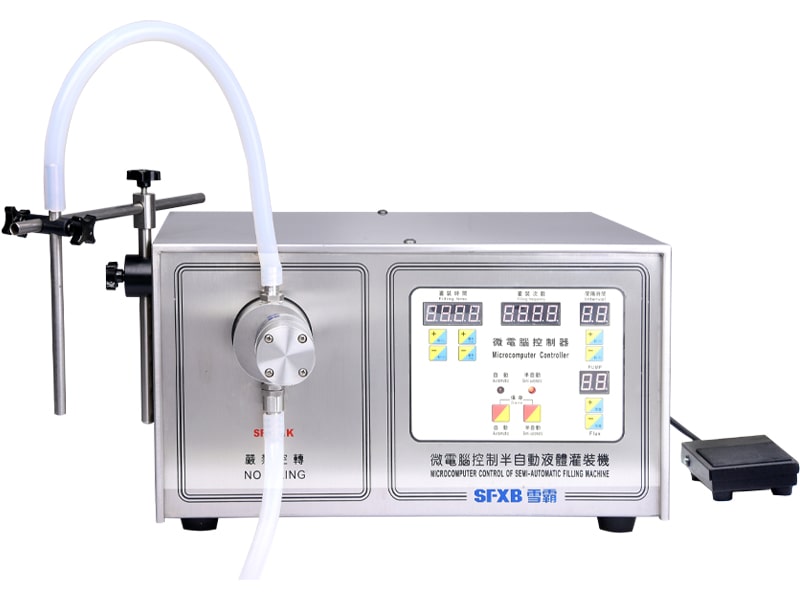
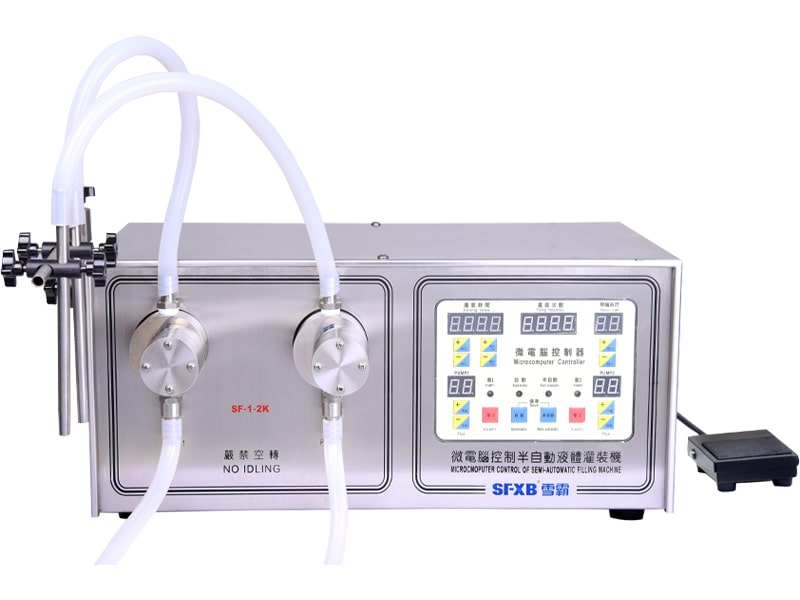
- Liquid products (water, oil, syrup, etc.) are commonly delivered by piston pumps, gear pumps, or peristaltic pumps. These devices draw a fixed volume from a reservoir (or hopper) and push it through the nozzle. For example, many bench-top liquid fillers use a servo-driven piston or diaphragm pump to achieve high accuracy.
 |
 |
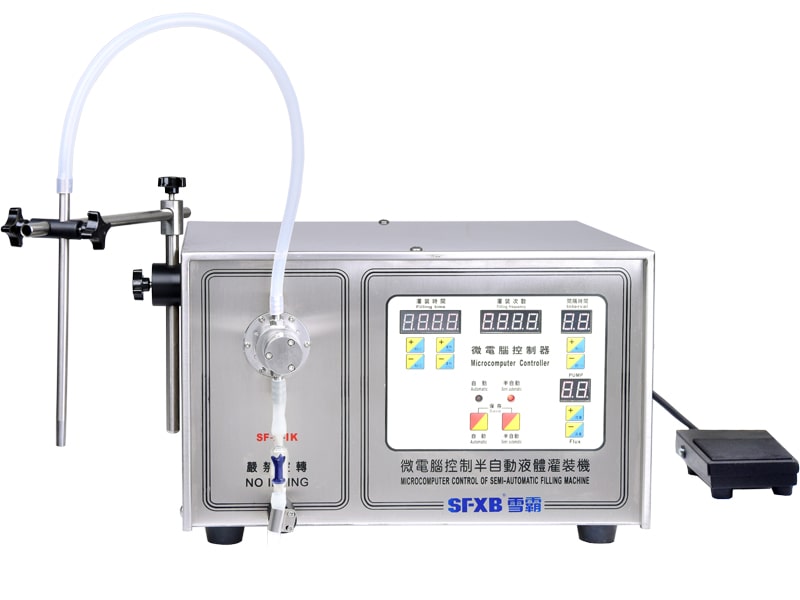 |
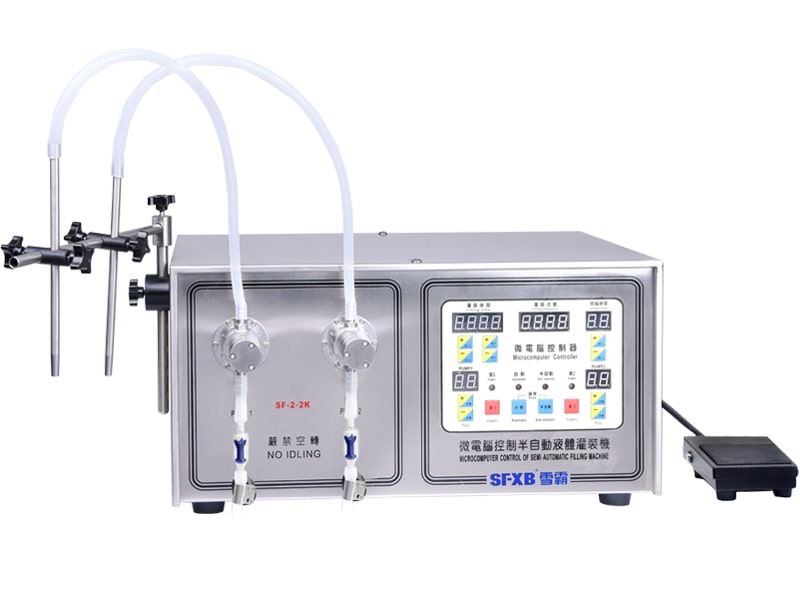 |
| SF-1-1/SF-1-2 Microcomputer Controlled Semi-automatic Liquid Filling Machine | SF-2-1/SF-2-2 microcomputer controlled semi-automatic liquid filling machine | ||
- Powders and granules are metered using an auger (screw) filler. In a semi-auto screw filler, the operator loads the powder into a hopper. Then a rotating screw discharges a precise amount into the container. The screw speed or angle can be adjusted so each bottle or jar receives the correct dose.
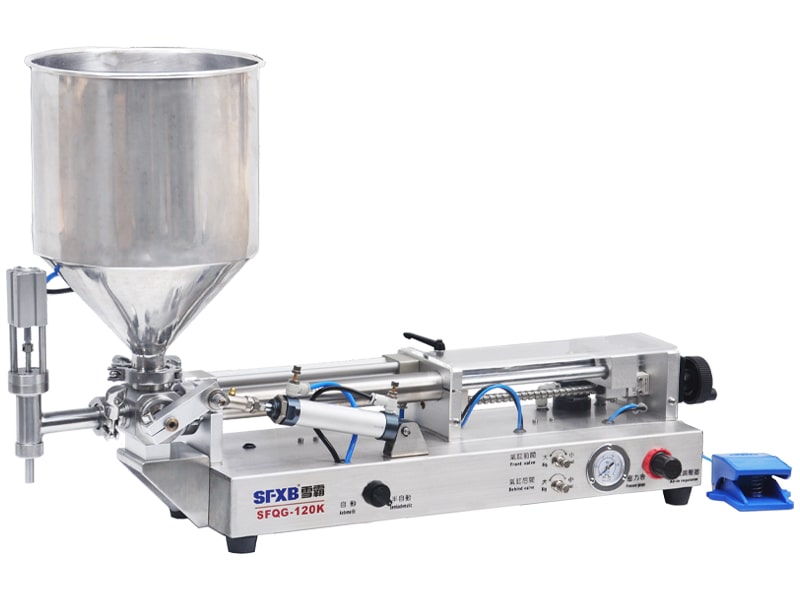
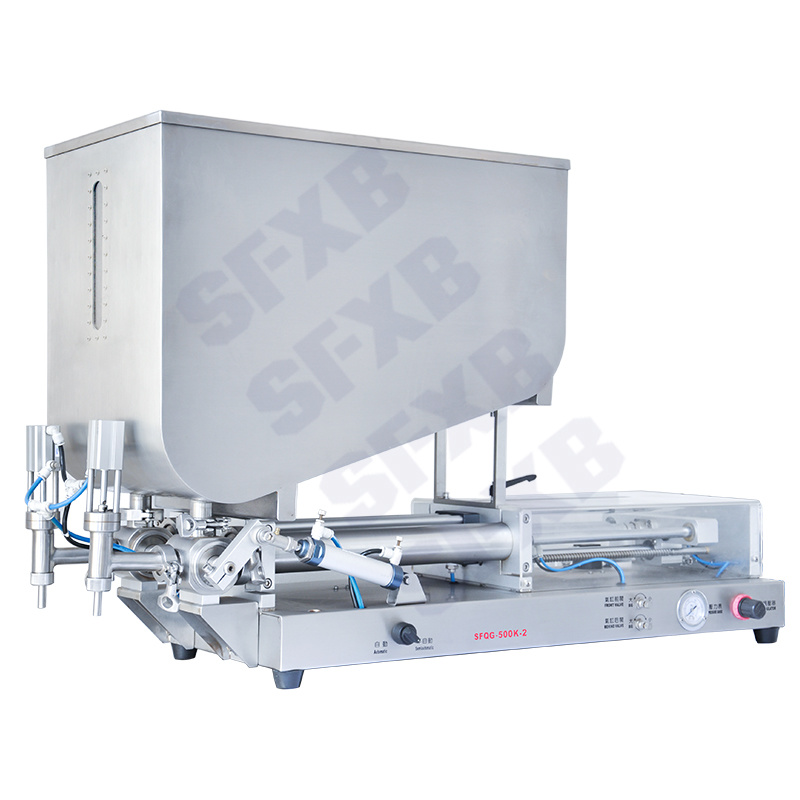
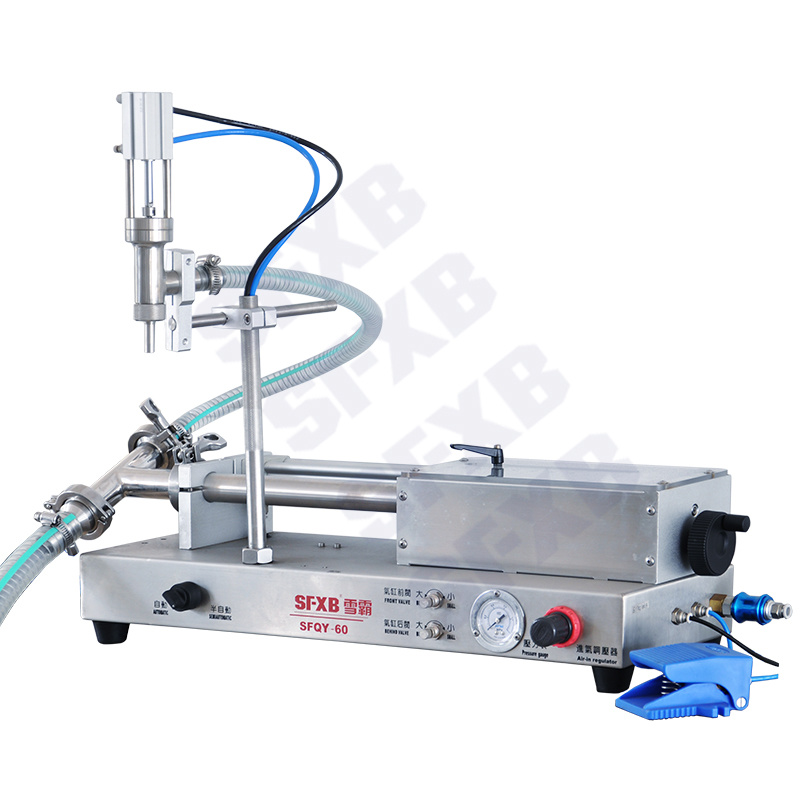
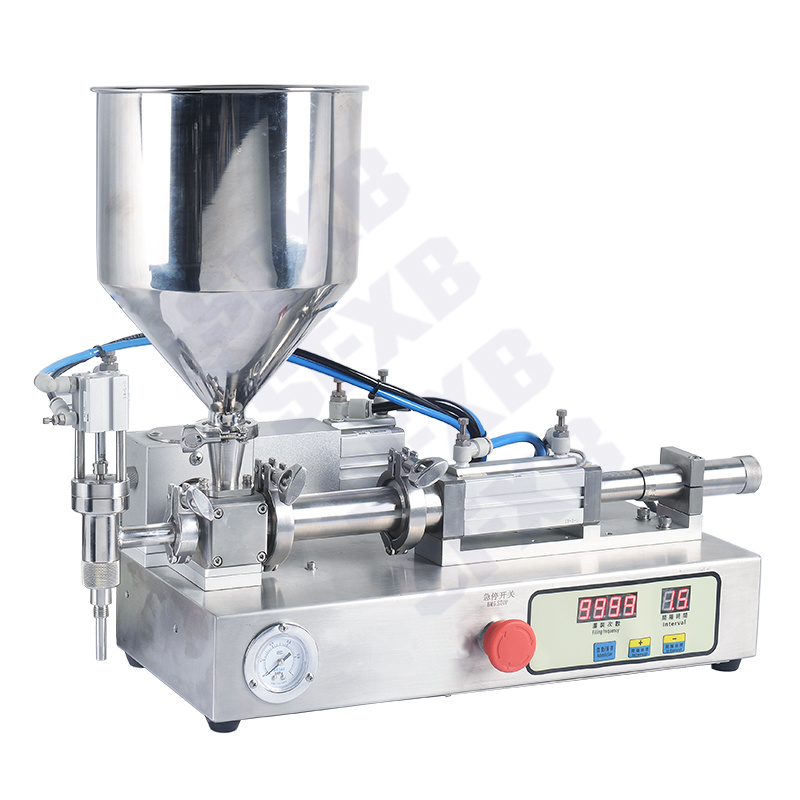
- Viscous creams and pastes (like honey or lotions) often use a pneumatic piston or even an air-driven reciprocating pump. A pneumatic filler (shown below) uses compressed air to drive the piston that injects the product. These machines can fill thick liquids or gels in accurate increments, and their simplicity makes them reliable in harsh or flammable environments.
 |
 |
 |
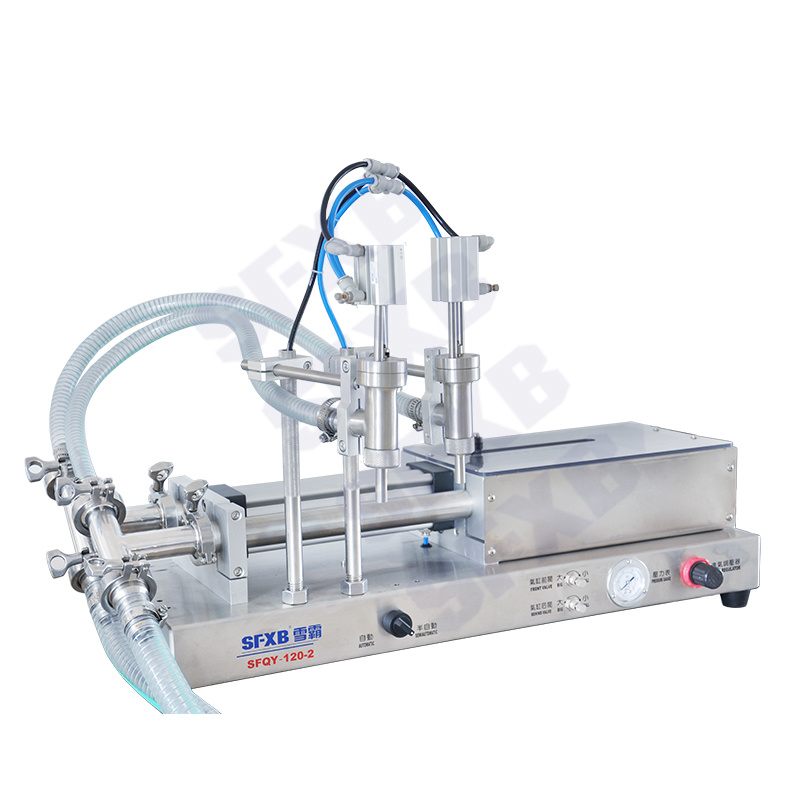 |
| SFQG series single-head/double-head fully pneumatic paste filling machine (explosion-proof) | SFQY series single-head/double-head full pneumatic liquid filling machine (explosion-proof) | ||
Example of a semi-automatic pneumatic piston filler with a large hopper. This machine is air-powered (no electricity at the nozzle) and is suited for viscous products. The operator uses a foot pedal or hand switch to trigger each fill, delivering an exact amount of paste or cream into tubes, jars or bottles. Semi-automatic paste filling machines (often pneumatic) are built for viscous foods and cosmetics. The product is gravity-fed from the hopper into a cylinder; pressing the pedal drives the piston to push out a fixed volume. Pneumatic models like this are chosen when safety or sterile conditions forbid electrical motors at the fill head.
Applications
Semi-automatic filling machines are widely used across industries that require precision but not ultra-high speed. Typical applications include:
- Food and Beverage: Filling bottles or jars with sauces, juices, oils, syrups, jams and other liquids or semi-liquids. Many small food processors use bench-top fillers for sauces and condiments. Auger fillers handle spices, coffee, sugar, or powdered mixes.
- Pharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals: Accurately dosing medications, supplements, or chemicals into vials, bottles, droppers or sachets. Semi-automatic fillers meet strict hygiene needs and ensure each container has the exact dosage.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care: Dispensing creams, lotions, serums, shampoos and makeup products into tubes, bottles or jars. These products often require gentle handling and precise volumes; semi-auto fillers maintain consistency batch-to-batch.
- Chemical Industry: Filling containers with adhesives, cleaning agents, paints or industrial liquids that may be hazardous. Semi-auto machines offer the needed accuracy while allowing an operator to oversee safety.
By the end of a production run, operators can maintain consistent fill levels and quality even for delicate or dangerous products. Many companies find that using semi-automatic fillers leads to less waste (no overfill), fewer labor hours per unit, and easier regulatory compliance compared to manual filling.
Advantages Over Manual Filling
Compared to hand-filling, semi-automatic machines provide clear benefits. They drastically reduce the drudgery and error rate of manual dosing. For instance, these machines “automate the filling, bottle positioning and capping steps” so an operator does not have to measure by hand each time. This automation doubles or triples throughput in many cases, with one operator overseeing several filling heads. The precision of mechanical pumps also means product quality improves: each container gets the intended volume without spillage or shortfills. Over the long run, businesses save on labor costs and material waste.
Semi-automatic machines also require lower upfront investment than full-automatic lines. This makes them ideal for startups or seasonal products. If needed, companies can later integrate an automatic conveyor or upgrade their fillers as demand grows. In short, semi-automatic fillers deliver many of the time-saving and accuracy benefits of automation, but with the flexibility and simplicity needed for smaller-scale or specialty production.
- Cost-Effectiveness:Semi-automatic filling machines typically require a lower capital investment and incur reduced operating costs compared to fully automatic lines, making them suitable for small to mid-sized production runs or businesses with budget constraints.
- Operational Ease:With straightforward controls and minimal setup requirements, these machines are user-friendly. Operators can learn to work with them quickly, reducing training time and dependence on specialized technicians.
- Flexibility:Designed to accommodate different container types and viscosities, semi-automatic filler nozzles and fixtures are often easily adjustable. This flexibility makes switching between products or jar sizes fast and efficient.
- High Precision:Leveraging volumetric (piston, gear, or peristaltic pumps) or gravimetric mechanisms, these machines ensure consistent fill volumes with high accuracy, reducing overfill, shrinkage, and product waste.
- Compact Footprint:Their bench-top or tabletop design makes semi-automatic fillers ideal for factories with limited floor space. They can be deployed quickly without complicating production layouts.
- Scalability:As production demands grow, semi-automatic machines can be upgraded—by adding fill heads, integrating PLCs, or connecting conveyors—to evolve into fully automated systems, protecting your original investment.
Choosing a Semi-Automatic Filling Machine
When selecting a semi-automatic filler, consider the following factors:
- Product Characteristics: Viscosity and particulate content determine the filling mechanism. (Thin liquids work well with timed-valve or piston fillers, while thick pastes need piston or pump fillers, and powders need auger screws.)
- Container Type: Bottle, tube, pouch, or jar? Ensure the machine’s platform and nozzles match your container design and fill level requirements.
- Production Volume: Semi-auto machines excel for small to medium batches. If you need hundreds of units per minute, an inline automatic line may be better.
- Materials and Safety: For corrosive or explosive materials, a pneumatic filling machine (compressed-air powered) is preferred. Stainless-steel contact parts are common for food/pharma.
Many manufacturers offer customizable semi-automatic fillers. For example, SFXB’s lineup includes both microprocessor-controlled liquid fillers and fully pneumatic explosion-proof models to suit different needs. By discussing your needs (product type, container, speed) with the supplier, you can find a semi-auto machine that balances cost, ease of use, and performance.
Conclusion
Semi-automatic filling machines bridge the gap between slow hand-filling and costly full automation. They provide repeatable accuracy, faster throughput, and lower labor requirements compared to manual methods. Yet they remain flexible and affordable for smaller production scales. Industries from food to pharmaceuticals rely on semi-auto fillers to package liquids, pastes, and powders efficiently. By automating the critical fill step, these machines enhance productivity and product consistency, often paying for themselves quickly in savings on labor and waste. When precise filling with human oversight is needed, a semi-automatic filling machine is an effective solution.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Semi-Automatic Filling Machines
1. What is a semi-automatic filling machine?
A semi-automatic filling machine automates the actual dosing of liquid, paste, or powder into containers, while still requiring an operator to position containers and activate the fill cycle. It balances efficiency and accuracy with human control.
2. How does it differ from a manual filling process?
Compared to manual filling, semi-automatic machines drastically increase speed, accuracy, and hygiene. They use pumps or pistons for precise dosing and require only minimal human input, eliminating risks of overfill or inconsistency.
3. What are the types of products a semi-automatic filling machine handles?
These machines can fill a wide range of products:
• Liquid filling machine – water, oil, syrups using gravity, piston, or vacuum filling.
• Paste filling machine – viscous items like creams and sauces using piston or pump systems.
• Powder/auger filler – dry products like sugar and spices using auger screws.
4. What is the role of a pneumatic filling machine?
A pneumatic filling machine uses compressed air to drive pistons or valves. It is ideal for flammable or sensitive products, as no electrical components are near the fill head, making it safer and more durable.
5. What types of filling mechanisms are used?
Common mechanisms include:
• Piston fillers – volumetric dosing via reciprocating piston .
• Gravity, overflow, or vacuum fillers – rely on gravity or vacuum to level-fill liquids .
• Auger fillers – metered powder dispensing via screw mechanism .
6. How accurate are these machines?
Semi-automatics offer consistent accuracy and repeatable volumes thanks to controlled pumps or pistons, with digital or mechanical adjustments ensuring precise fill levels.
7. What production scale is appropriate for semi-automatic machines?
They are ideal for small to medium production volumes, seasonal batches, R&D, pilot runs, or businesses needing flexibility—offering faster turnaround and quality compared to manual filling.
8. Can they handle different container types?
Yes. Semi-automatics can adapt to bottles, jars, tubes, pouches, and more. Many models allow rapid nozzle adjustment and quick changeover between various container sizes.
9. Are they easy to maintain and clean?
Semi-automatic machines are generally low-maintenance. They’re compact, have fewer moving parts than full-automatic lines, and are often designed for easy disassembly and cleaning—meeting hygiene standards.
10. Can a semi-automatic filler be upgraded later?
Absolutely. Many can be enhanced with extra fill heads, PLC control, conveyors, or full automation down the line. This scalability makes them cost-effective for growing operations.
| References: | |
| 1. | A Technical Guide to Automatic and Semi-Automatic Filling Machines ——Retrieved from:ResearchGate |
| 2. | Comprehensive Analysis of Semi Automatic Multi Head Filling Machines Market Profitable Key Business Trends Growth Rate ——Retrieved from:LinkedIn |







Comments