Food packaging machines are specialized industrial systems designed to efficiently pack and seal food products in a hygienic, automated manner. They protect food from contamination and extend shelf life by providing airtight or tamper-evident packages. In modern food production, practically every packaged food item (beyond fresh fruit or produce) passes through automated packaging equipment. For example, one industry source notes that “regardless of the food type, this packing is done with an automated food packaging machine”, highlighting how ubiquitous these machines have become in food processing lines.

The global food packaging machinery market is growing rapidly. Industry reports estimate it was worth about USD 19.9 billion in 2023, with forecasts projecting around USD 30.9 billion by 2034. This expansion is driven by rising processed-food consumption and the need to package large volumes quickly. Automated machines do not get fatigued or introduce contaminants; they can run continuously with consistent precision. For example, packaging systems can operate for hours without quality variation, unlike manual labor, which helps eliminate bottlenecks and hygiene risks on the line.
In this guide, we explore the main types of food packaging machines, from primary packagers (like vacuum sealers and form-fill-seal systems) to secondary and end-of-line equipment (cartoners, case packers, etc.). We will explain how each machine works and why it’s used, providing a science-based overview to help manufacturers choose the right solution.
Vacuum Packaging Machines
Vacuum packaging machines remove air from the package and then seal it tightly. This is especially effective for highly perishable foods such as fresh meats, cheeses, or cooked meals. By eliminating oxygen, vacuum sealing inhibits aerobic bacterial growth and oxidation, dramatically slowing spoilage. For instance, vacuum sealers can preserve food up to 3–5 times longer than ordinary storage conditions. In fact, industry sources note that perishable items (e.g. fresh meats, frozen foods) are “best vacuum packed” because this process can “tremendously extend storage life”. In practice, vacuum machines are widely used for products destined for freezer display or long-term storage. Some advanced vacuum packagers also support modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) by injecting inert gas (like nitrogen) before sealing, further prolonging shelf life without using chemicals.
Flow Wrapping Machines
Flow wrapping machines (a type of horizontal form-fill-seal system) wrap products in a continuous plastic film. In a flow wrapper, individual items are fed on a conveyor into a tube of film, which is then sealed on both sides to form a “pillow” package. This horizontal motion is very versatile: it works for solid food bars, biscuits, confectionery, frozen meats, and many other products. Flow wrappers offer high speed – entry-level machines can run 50–150 packages per minute, while high-end industrial models can exceed 1,000 packages per minute. The resulting packages are airtight and moisture-resistant, protecting contents from dust and oxygen. By keeping packages hermetically sealed, flow wrapping helps maintain freshness and product quality. Many manufacturers also print branding or instructions on the film before sealing, maximizing shelf appeal.
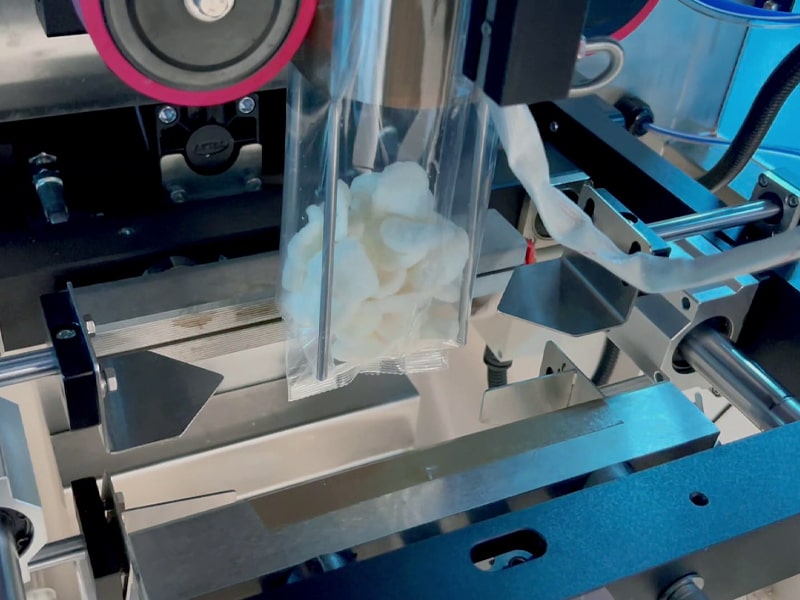
Vertical Form-Fill-Seal (VFFS) Machines
Vertical form-fill-seal machines create bags in a vertical orientation using roll stock film. In a VFFS machine, a roll of plastic (or laminated) film is shaped into a pouch around a forming tube. The machine then fills the pouch with product and seals the top, all in one continuous motion. These machines start with a large roll of film, form it into a bag shape, fill the bag with product, and seal it – typically at speeds up to 300 bags per minute. VFFS lines are prized for their efficiency and space-saving footprint; they are “fast, economical packaging solutions that conserve valuable plant floor space”. They can use a wide variety of films (polyethylene, foil laminates, etc.) and form factors (flat, gusseted, stand-up pouches). Common applications include powders, grains, nuts, snacks, and any free-flowing product where a sealed pouch or bag is desired.
Bagging Machines
Bagging machines (often called open-mouth baggers) fill pre-made bags or pouches with product and then seal them. This approach is popular for bulk dry foods. Foods like rice, flour, sugar, cereals, pet foods and powdered mixes are often packed in bags or sacks by these machines. In a typical bagging line, product is measured (for example by a scale or multi-head weigher) and fed into an open bag. The bag is then closed by heat-sealing, stitching, or another method. For high accuracy, manufacturers use precision weighers; for example, Ishida – a leading packaging-equipment brand – offers multi-head weighers that feed bagging machines to ensure each bag contains exactly the right weight. Packaging sources note that bagging machines are “common to pack cereals and powdered foods”. High-speed baggers can handle hundreds of bags per minute, and they ensure gentle handling for delicate products. After filling, the bags are typically sent to a conveyor or palletizer for batch shipping.
Filling, Capping and Sealing Systems
For liquid or bottled foods, specialized filling and capping machines are used. Filling machines accurately dispense beverages, sauces, dairy, or other liquids into bottles, jars or containers. They may use gravity, piston pumps, or volumetric mechanisms depending on fluid type. After filling, capping machines automatically apply caps or lids. Packaging industry sources explain that capping machines “close bottled food items by placing air-tight caps,” especially in soda, syrup, and drink lines. In practice, a beverage line might have an accumulator conveyor to line up bottles, a liquid filler station, a capper, and then a labeler. The accumulator (or “infeed” conveyor) spaces and aligns containers so the filler and capper can work at top speed. Together, these machines form a continuous liquid packing line – from raw bottles to sealed, labeled products – with minimal human intervention. They ensure each container is filled to the correct level and sealed properly, which is critical for food safety and shelf life.
Checkweighers and Inspection Equipment
Quality and safety inspection machines complement the packaging line. Checkweighers are high-speed scales placed after filling to verify each package’s weight. Every item is weighed, and any under- or over-weight package is ejected from the line. According to packaging experts, checkweighers “can weigh hundreds of items per minute” and ensure that each product is at the correct target weight. This prevents regulatory issues and avoids product giveaway by enforcing strict weight consistency. Likewise, food factories often use metal detectors or X-ray inspection systems to catch foreign objects, and vision systems to check fill levels or label placement. Although these devices are technically separate from the packagers, they are integral to a complete packaging line. Together, this inspection equipment helps maintain the high quality and safety standards demanded for food products.
Secondary Packaging and End-of-Line Equipment
After primary packaging, secondary and tertiary machines handle grouping and shipping. Case packers or cartoners automatically load finished products into cardboard boxes or cartons. For example, robotic case packing machines pick sealed packages and place them into trays or cases. As one industry guide notes, case packers are typically “used for secondary packaging of food products” – meaning the product is already bagged or potted, and the machine simply arranges them into cases. Following cartoning, palletizing systems stack the filled cases onto wooden pallets. Modern palletizers often use robotic arms or gantry robots to quickly and precisely arrange cartons into stable stacks. Finally, many plants use shrink-wrappers or stretch-wrap machines to wrap the loaded pallet for transit, ensuring the load stays secure. Additionally, bundling (banding) machines can wrap multiple products together: for instance, they may group several candy bars or snack packages into one bundle with a plastic band. These secondary machines prepare products for distribution while maintaining organization and protection.
Automation and Industry Trends
Food packaging machinery is becoming increasingly automated and smart. Robotics, sensors and software are incorporated at every step. Pick-and-place robots can transfer items between machines or load cartons; delta robots and cobots handle very fast or delicate packing tasks. Automation provides many benefits: higher throughput (machines can handle tens of items at a time far beyond human speed), improved safety (robots handle hazardous tasks, reducing injuries), and consistent quality (machines eliminate human variability for identical packages). For example, automated case packers and palletizers can organize loads in seconds with exact precision, boosting output. Other trends include IoT connectivity (machines report status and metrics), and traceability features (automatic date/lot coding on packages). Many manufacturers now integrate full data tracking, so every package is labeled and recorded for quality control.
Key benefits of automation include:
- Increased productivity: Automated lines can process far more packages per minute than manual operations.
- Enhanced safety: Automating repetitive or dangerous tasks (like hot sealing or heavy lifting) protects workers.
- Uniform quality: Machine precision yields packages that are identical in weight, seal integrity, and appearance.
- Lower operating cost: After the initial investment, machines mainly require electricity and minimal upkeep, often costing less than ongoing labor.
- Full traceability: Integrated printers and vision systems can print barcodes or batch codes on each package and store production data, meeting modern food safety standards.
These trends mean that today’s food packaging machines not only wrap and seal, but also collect data, adapt to different products quickly, and work almost autonomously.
Selecting the Right Packaging Machinery
Choosing the optimal packaging equipment depends on your product and objectives. Consider the type of product (liquid, powder, solid, fragile), desired pack size and format, required speed, and budget. For example, powdered foods often use VFFS baggers, whereas rigid containers may need rotary fillers. Businesses also evaluate long-term costs: a faster, more durable machine may cost more upfront but save money over time. SFXB experts advise assessing factors such as cost of ownership, production efficiency, customization options, customer support, and quality control when selecting a vendor. Reputable manufacturers usually offer customization (e.g. adjustable bag sizes or multi-format lines) and strong after-sales service. Ultimately, the best packaging machine is one that matches the product’s needs, fits the production volume, and complies with food-safety regulations.
By understanding these various machine types and their applications, food producers can design an optimal packaging line. The right equipment will boost throughput, maintain product quality, and enhance competitiveness in the global market. As technology advances, we expect packaging machines to become even more flexible, efficient, and intelligent – helping manufacturers meet growing demand for safe, well-packaged food.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Food Packaging Machines
1. What is a food packaging machine and why is it essential?
Answer: A food packaging machine automates the process of packing food products—such as sealing, wrapping, bagging, or boxing—to extend shelf life, ensure food safety, and improve production efficiency. Compared to manual packing, automated systems provide consistent sealing quality, reduce contamination risk, and support high-speed output.
2. What types of food packaging machines are available?
Answer: Common types include:
• Vacuum packaging machines
• Flow wrapping (horizontal form-fill-seal) machines
• VFFS (vertical form-fill-seal) machines
• Open-mouth baggers
• Liquid filling and capping systems
• Cartoners and case packers
• Checkweighers and inspection systems
• Shrink-wrappers, palletizers, bundlers
• Each type suits specific product formats and production needs.
3. What is a VFFS machine and how does it work?
Answer: VFFS (Vertical Form-Fill-Seal) machines form bags from roll-stock film, fill them with the product, and seal them—all in a continuous vertical motion. They operate by unwinding film, forming a tube around a collar, sealing vertically, filling, then sealing/cutting horizontally at speeds up to 300 bags/minute.
4. What are the advantages of using an automatic food packaging machine?
Answer: Benefits include:
• High production speed (50–1000+ packages/minute)
• Consistent seal quality
• Lower labor costs
• Improved hygiene and reduced contamination
• Traceability with inkjet coding and sensors
• Easier scalability and quicker changeovers
5. How often should food packaging machines be serviced and maintained?
Answer: Maintenance schedules depend on machine type, usage frequency, and environment. A general guideline suggests monthly or quarterly preventive inspections, focusing on belts, seals, bearings, blades, and moving parts. Proactive maintenance minimizes downtime and extends equipment life.
6. What is Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) and when is it used?
Answer: MAP injects inert gases (e.g., nitrogen) into packages before sealing to reduce oxidation and microbial activity. Typically applied in flow wrapping and VFFS systems, MAP extends shelf life without preservatives, making it ideal for fresh meats, cheese, and sensitive foods.
7. How do I choose the right packaging machine for my product?
Answer: Consider factors including:
• Product type (liquid, powder, solid)
• Desired bag/container format and size
• Production volume and speed requirements
• Budget and total cost of ownership
• Hygiene, regulatory compliance, and after‑sales service.
8. What is the difference between volumetric and gravimetric filling?
Answer:
• Volumetric filling dispenses a preset volume to meet a target weight, suitable for consistent-density products.
• Gravimetric filling measures weight directly via scale control, offering higher accuracy for variable-density products.
9. Can packaging machines handle multiple package sizes or SKUs?
Answer: Yes. Many modern machines support quick changeovers or automated adjustments to accommodate different mandrel/collar sizes, film widths, or bag dimensions. Digital memory systems can store multiple SKU formats for efficient transitions.
10. Are food packaging materials always food-safe?
Answer: Only certified materials (e.g., plastic films, laminates, foils) with food-contact approval should be used. Look for symbols like the wine-glass/fork icon—required in EU and recognized worldwide—that indicate compliance with safety regulations.
| References: | |
| 1. | Food Packaging Equipment Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report ——Retrieved from:GrandViewResearch |
| 2. | Vertical form fill sealing machine ——Retrieved from:Wikipedia |
| 3. | The benefits of vacuum packing in food packaging ——Retrieved from:Packaging-gateway |






Comments